According to (Solomon 2006) learning refers to a permanent change in behaviour which comes with experience. This does not necessarily have to affect the learner directly, people can also learn by watching others. For example if two children are playing inside the house and one of them throws a ball and breaks a vase and gets in trouble for it, not only would that child not do it again nor would the other one.
The dictionary defines learning as ' an act, process, or experience of gaining knowledge or skills. http://www.thefreedictionary.com. People can also learn unknowingly, it happens even if we are not trying to, for example we may recognise or sing along to slogans or songs that we don't even like or have never used before. Learning is an ongoing process as we are continuously having to re-evaluate the environment around us due to the constant new stimulus that we are exposed to.
There are several different approaches to learning, all of which have something to contribute but have different significances for different contexts. These learning styles consists of three main groups; humanistic, cognitive and behavioural all of which believe that there are key characteristics to determine the way in which a person learns.
The behaviourist theorists believe that behaviour can be researched scientifically ignoring any aspects of the mind. One of the views from behaviourist theorists is that all behaviour is determined by the environment either by association or by reinforcement and nothing to do with free will. There are two theories that psychologists often refer to when looking at learning in this perceptive, the classical conditioning and operant theory.
The classical conditioning theory was instigated by Ivan Pavlov, who focused on the observable behaviour he argued that human thinking is down to association. "Beyond association there is nothing more in it" (Pavlov 1955) The classical conditioning theory which has since become very influential within children's psychology.
Pavlov induced classically conditioned learning by pairing a netural stimulus (a bell) with a stimulus known to cause a salivation response in dogs (he squirted dried meat powder into their mouths). The powder was an unconditioned stimulus because it was naturally capable of causing a response. Over time the bell became a conditioned stimulus, it did not initially cause salvation, but the dogs learnt to associate the bell with the meat powder thus salivating at the sound of the bell only. (Solomon 2006)
Operant conditioning is learning through reinforcement in that an individual is either rewarded or punished for participating in a certain action, they learn that what ever the action is that they have done they will either carry on doing so or stop because of the consequences. For example when children are in school they get rewards for doing good work such as stickers or merits etc to encourage them to carry on working hard whereas if they are naughty they get punished with detentions, suspensions and put in isolation rooms to make them not do it again.
B.F. Skinner is known for conducting an experiment which looked to find out about operant conditioning, this experiment involved the use of rats in boxes, in which there was a lever that when the rat pushed it it would release some food. However the rats did not know this thus making the only way for them to find out through trial and error so that the rats would eventually learn that by pressing the button the would get some food, making the food the reinforcer and the lever the operant. .F. Skinner introduced the theory operant conditioning which is the process in which the individual learns to perform behaviours that produce positive outcomes and to avoid those that yield negative outcomes.
I have found an clip that demonstrates this process
Marketers have taken on this concept by introducing consumer reward schemes, the first company that demonstrated this were Tesco's but since then it has become a common and successful way of implementing consumer loyalty. Companies such as Boots, Sainsburys and even Orange have these reward schemes with Orange doing an orange Wednesday whereby their consumers get a buy one get one free cinema offer.
Marketers have taken on the concept of the classical conditioning theory in that, over time they can create an image for the product or brand that will then be associated with it. This can be seen with some brands nowadays such as;
Bounty who have the association of being tropical and exotic.


Nike who have the association of being winners

"Learning is the acquisition of knowledge and memory is the storage of internal representation of that knowledge" (Blakemore 1988) "Without memory we would be servants of the moment, relying on reflexes. Civiliastion itself is the distillation of human memory"
Without our memories it would be impossible to learn, as it plays a huge role in our learning process especially within the behaviourist theories., if we couldn't remember how would we learn what was right and wrong and also reward schemes would prove to be irrelevant as we wouldn't be able to remember any on the consequences.
'Memory involves a process of acquiring information and storing it over time so that it will be available when needed' (Solomon 2006). So basically when you see something or are told something for example a TV advertisement, the information that you have gained will be stored until you need it again. However in order to retrieve this memory there is a process to get it back.
The Memory Process

This model shows the process in which whenever an individual is given a new piece of information that they then may need to retrieve in the future they have to go through various stages. In order for these memories to be recalled at a later date the individual needs to have rehearsed the memory over time.
To see how this work, I done a memory test which involved looking at a shopping list for 10 seconds, and then after writing down as many items that you could remember. There were 10 items on the list which were;
- Paper Clips
- Matches
- Socks
- Hat
- Blouse
- Tie
- Picture Frames
- Light Bulbs
- Petrol
- Stamps
Our senses play a significant role on recalling our memories, as through this we can relate back to a moment that has previously happened. For example a song could bring back a memory of something that you had done or a smell whether it be a positive or negative memory for example the smell of hospitals may bring back a negative experience of the time that you had spent there.
For myself certain songs, or places, or television shows bring back memories from my younger years mostly positive but sometimes negative too.
A process has been identified which shows the various different memory systems to help us understand the relationship between them, as there is sensory memory that an individual has that will help identify objects when seen, heard or touched for the first time. The short-term memory which vary in the amount of information that can be stored and the length of time. Lastly long-term memory which allows us to retain information for long periods of time, in order for this to work a lot of rehearsal of the memory is required. These can all be seen in the diagram below;
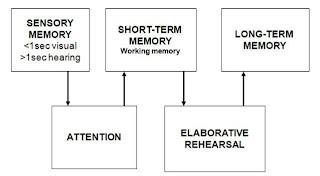
Nostalgia is described as 'a wistful desire to return in thought or in fact to a former time in ones life' (http:www.dictionary.com). It has also been described as 'a bitter sweet emotion where the past is viewed with both sadness and longing.' (Solomon 2006) Nostalgia can refer make to memory in that it is the emotions and the recall from seeing or hearing something that you have a memory for, the difference being its a very positive thing whereas with memories alone it can create negative feelings towards something. Marketers can take advantage of this as when targeting to specific age groups they can put something in that everyone will relate to thus making them more likely to remember the brand that was advertised or buy into their products.
I have done a mood board to show the things that make me nostalgic


No comments:
Post a Comment